Child Development
Thursday, April 27, 2006
Pregnancy and childbirth
natural or with meds--midwife or OB/GYN
problem pregnancy (diabetes, STD, older, teens)--genetic counselor
stress--ob/gyn or psychologist
addictions (high risk)--ob/gyn or psychologist
religious/racial differences between parents--priest/pastor/rabbi
pain management--Lamaze instructor
different types of births--OB/GYN
premature births--OB/GYN
multiple births--OB/GYN
infertililty--fertility specialist
types of conception--fertility specialist, OB/GYN
adoption--lawyer, social worker, OB/GYN, planned parenthood
breastfeeding--nurse, lactation consultant
Infancy and Toddlerhood
teething--RN
potty training--pediatrician, child care worker
speech and language development--speech therapist
walking--physical therapist
scheduling--pediatrician
socializing--teacher (daycare/extracurricular)
diet--nutritionist
behavior--daycare teacher, behaviorist
breastfeeding--lactation consultant
Early Childhood
discipline--psychiatrist (?)
potty training--pediatrician
transition to school--teacher
communicating--psychiatrist (?)
eating--nutrition specialist
sleeping on own--pediatrician
Sunday, April 23, 2006
Thursday, April 20, 2006
Piaget's Cognitive-developmental theory
Sensorimotor Stage
Schemes
Assimilation and Accomodation
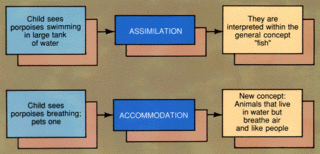
Circular Reactions
 Object Permanence
Object PermanenceA-not-B search error
deferred imitation
functional play
make-believe play
violation-of expectation method
Infant memory
Recognition and recall
Infantile amnesia
Autobiographical memory
Vygotsky's Zone of Proximal Development
Infant Intelligence Tests
Bayley Scales of Infant Development
Mental scale and motor scale
Developmental Quotient
Home Observation for Measurement
Language Development
Behaviorist perspective
Nativist perspective
language acquisition device
Interactionist perspective
Cooing and babbling
joint attention
underextension
overextension
telegraphic speech
child-directed speech
Erikson's basic trust versus mistrust
autonomy versus shame and doubt
basic emotions
social smile
stranger anxiety
separation anxiety
social referencing
self-conscious emotions
emotional self-regulation
Temperament
Easy, difficult, and slow-to-warm-up children
inhibited and uninhibited children
goodness-of-fit model
attachment


Ainsworth's Strange Situation
secure attachment
avoidant attachment
resistant attachment
disorganized/disoriented attachment
Attachment Q-sort
fathers, siblings and child care
attachment and later development
I-self and me-self
empathy
self-control
compliance
Physical Growth in Early Childhood
Handedness
Dominant Cerebral Hemisphere
Nightmares and Sleep Terrors
Eating habits in early childhood
Gross and fine motor skills
Preoperational thought
sociodramatic play
dual representation
operations
egocentrism (link)
animistic thinking
conservation (link link)
centration
irreversibility
hierarchical classification
class inclusion problem (link)
Understanding death
1. permanence
2. universality
3. nonfunctionality
Piaget and Early Childhood Education
1. Discovery learning
2. Sensitivity to children's readiness to learn
Vygotsky and private speech
Scaffolding
Vygotsky and Early Childhood Education
Information Processing
Planning
Memory strategies
Episodic memory
scripts
Metacognition
Theory of Mind
Ordinality and cardinality
Power Point
Physical Knowledge in Infancy
Obituary of Urie Bronfenbrenner
The Nature of Love by Harry F. Harlow (1958)
Tuesday, April 18, 2006
Explain why breastfeeding (or choosing not to breastfeed) can have lifelong consequences for the development of babies born in poverty-stricken regions of the world. (Use the information on page 178 to answer this question).
Physical Development in the First Two Years
Physical growth--height and weight

Cephalocaudal trend
Proximodistal trend
fontanels
teeth
neurons
lateralization
brain plasticity
changing states of arousal/sleep habits
breastfeeding and bottlefeeding
nonorganic failure to thrive
classical conditioning
UCS-UCR CS-CR
operant conditioning
habituation and recovery
imitation
motor development average age of walking
ulnar grasp
pincer grasp
hearing
vision
visual cliff
Babies and Their Senses
Thursday, April 06, 2006
Genetic environmental correlations. For either yourself or a child you know, give examples of passive, evocative, and active (niche-picking) genetic environmental correlations. See pages 86 and 87 for the definitions and some examples, but in your reaction paper, be sure to give examples of each type of correlation specific to the child you are describing. Due April 11.
The paper should be in APA format (see resources below). Pages should have one-inch margins on all sides, and in addition to the 5 pages of text, you should have a cover sheet and a reference page. At least one of your sources should be a psychological journal.
Your paper should do the following:
1. Provide a general overview the stage of development you will be discussing in your paper. For example, if your topic is kindergarten readiness, set the stage for your paper by describing some of the advances that take place in early childhood. One way to do this might be to devote a paragraph each to physical, cognitive, and social development during that stage. You may use your textbook as the reference for this section, or a different textbook if you prefer, but be sure to actually use a scholarly source for your description of that stage of development.
2. Next, present the main topic of your paper, explaining why it is an important issue in development. Again, any facts or assertions you present should be backed up by a citation. See the links below for information on how to cite your sources throughout the body of your paper.
3. Present information from an interview with a person who works professionally with the issue and age group, or is in some way an "expert" in this area. This should not be more than 1 1/2 pages of your paper, and you should be sure to tie it in to the broader context of your paper. When you tell me what topic you have decided on for your paper, I would be happy to discuss ideas for questions and/or the general direction your interview might take.
4. Your summary and conclusion, including any recommendations you have. This would be the part where you might add your personal thoughts on the subject, as well as what you have learned from the process of writing this paper.
Resources:
Psychology journals and resources for colleges, teachers and their students.
Writing Center and APA style writing help provided by AlleyDog.com
Period of the zygote
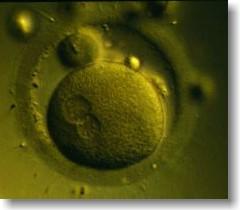

Implantation

Period of the embryo



Period of the fetus

age of viability
Teratogens
Thalidomide
Tobacco
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome

National Geographic Article
Fetal Alcohol Effects
Rubella
HIV/AIDS
Toxoplasmosis
Exercise
Nutrition
Folic Acid
Stress
Rh factor incompatibility
Toxemia
Chapter 4
first, second, and third stage of labor

dilation and effacement of the cervix

transition
Apgar scale
Natural, or prepared, childbirth
Certified nurse-midwife
Average weight and length of newborns
Vacuum extractor
Forceps

Induced labor
Breech position
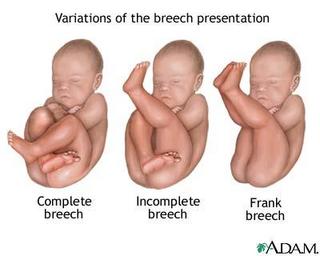

Cesarean delivery


Anoxia and cerebral palsy
Respiriatory distress syndrome
Preterm and small-for-date babies
Post-term babies
bonding
rooming in
Reflexes: rooting

Moro

palmar grasp
stepping

Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale
Sleep
Cying
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
The senses at birth
Visual Cliff

Interview with Lennart Nilsson
NOVA Online: Life's Greatest Miracle
Medline Plus Pregnancy Articles
Pregnancy.org Fetal Development
Benefits of Kangaroo Care for Preemies
Virtual Children's Hospital: What Is Kangaroo Care?
Twins by Different Fathers
Artificial Insemination Articles from the New York Times
How Stuff Works--Twins
Alice and Emma (Preemie twins born 39 days apart)
